Empathy in technology means creating experiences that understand and respond to human feelings. It's more than just user-friendly design; it's about creating a connection. As technology advances, our interaction with it also changes. Once a tool for specific tasks, technology integrates deeply into our daily lives. This integration calls for a more human-centric approach.
Steve Jobs once said, "Technology is nothing. What's important is that you have faith in people, that they're good and smart, and if you give them tools, they'll do wonderful things with them." This quote highlights the essence of empathetic user experiences. They are about understanding users' needs and resonating with their emotions.
The challenge lies in designing technology that feels less like a machine and more like a companion that recognizes and adapts to our emotions. This need guides us toward more intuitive, responsive, and emotionally aware technological interactions.
So, let's talk more about the need to create empathetic user experiences online.
The Importance of Empathy in User Experience
Empathy in user experience leads to profound psychological impacts. Users feel understood, valued, and connected to the product or service. Microsoft showcases this through its Microsoft Garage program. Employees from any department can develop projects outside their primary job.
Another example is Facebook. They offer flexible work hours, aligning work with lifestyle. This approach makes employees feel respected and understood. The result is a more dedicated workforce that creates empathetic user experiences.
These case studies directly link empathetic policies and increased user satisfaction. Empathy leads to loyalty. Users appreciate products and services that understand their needs and emotions. Empathetic design is not just a nice-to-have. It is essential for building lasting relationships with users.
Understanding User Needs and Emotions
Understanding user emotions is crucial in designing empathetic experiences. User research methods like interviews, surveys, and observations reveal diverse emotional needs across different demographics for inclusive design. You need to remember that emotions are dynamic that change over time. This adds complexity to empathetic design and shows the need for continuous user engagement.
Developing personas helps designers visualize the target audience as real, relatable individuals. However, you must apply personas practically. They should form a part of design decisions as they help designers get emotional insights that translate into meaningful user experiences.
"Everything has a personality: everything sends an emotional signal. Even where this was not the intention of the designer, the people who view the website infer personalities and experience emotions."
— Don Norman, Grand old man of UX design
Empathy maps are vital as they capture what users say, do, think, and feel. They show insights into their emotional worlds.
- Says Quadrant: Includes direct user quotes. It reveals their explicit thoughts and verbal expressions from interviews or usability studies.
- Thinks Quadrant: Captures the user's internal thoughts and concerns. It focuses on what they might think but not necessarily express openly.
- Does Quadrant: Encompasses the user's actions and behaviors. It shows what users physically do while interacting with the product or service.
- Feels Quadrant: Reflects the user's emotional state and describes their feelings about their experience, often conveyed through adjectives and contextual sentences.
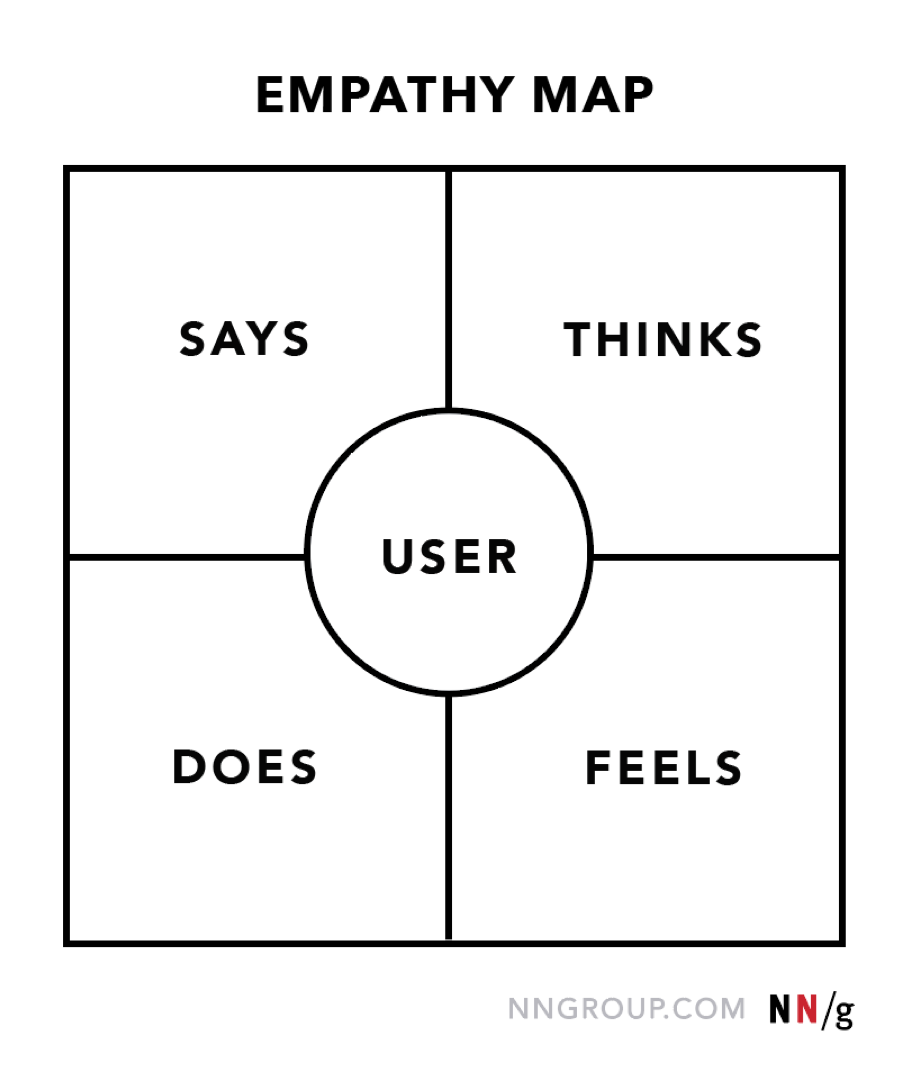
But, designers must be aware of their limitations. Empathy maps rely on subjective interpretation and should be used alongside other methods to validate emotional understanding.
Incorporating Emotional Design Principles
Incorporating emotional design principles enhances user experience significantly. Here are some key aspects:
- Color: Colors evoke emotions. Bright colors can energize, while muted tones often soothe. Choose colors that align with the emotional tone of your product.
- Typography: The style of the text affects how users feel. Bold, large fonts can convey strength and confidence. Script fonts often feel personal and intimate.
- Imagery: Images trigger emotional responses. Use visuals that reflect the user's desires and aspirations. Align imagery with the overall emotional message of your product.
Crafting narratives that resonate emotionally is crucial. Stories connect users to products on a deeper level. They create a sense of belonging and understanding.
Personalization and customization play a vital role. Tailored experiences make users feel valued and understood. They show that the product or service adapts to their unique needs and preferences. This approach leads to stronger emotional connections and enhanced user satisfaction.
Amazon exemplifies the pinnacle of website personalization. Known for its tailored user experience, Amazon's homepage features personalized recommendations and content based on each customer's unique profile.
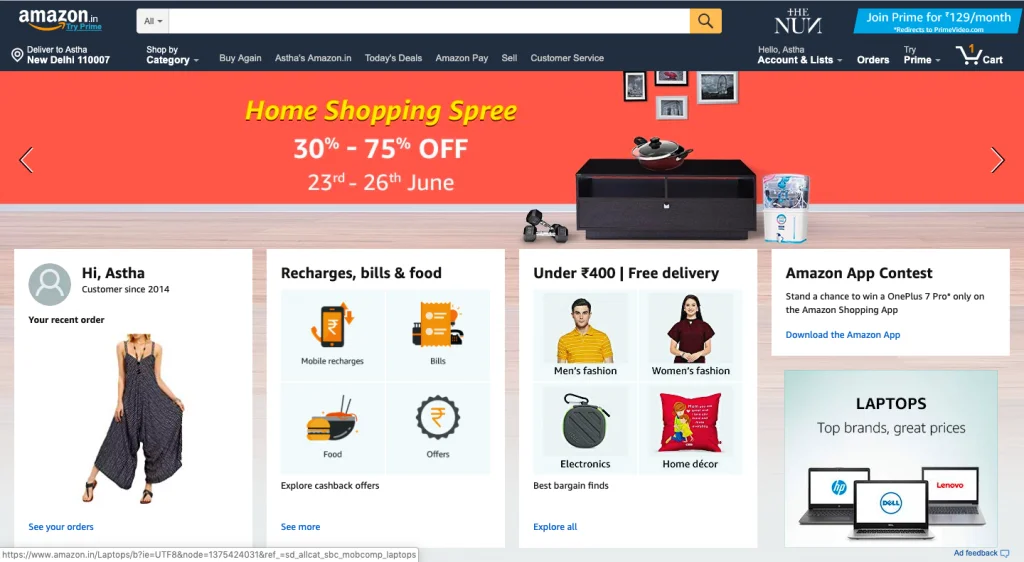
With most users having an Amazon account, the company leverages extensive customer data, including name and address, to customize its interface. It finely tunes product recommendations based on visitors' browsing behavior and purchases. This approach ensures that each user's recommendations truly reflect their specific interests.
Technological Empathy in Interaction Design
Technological empathy in interaction design refers to the capability of digital systems to understand and respond to user emotions and needs. It involves designing technology that functions efficiently and connects with users on an emotional level. This approach makes digital interactions feel more natural and human-like.
Integrating AI and machine learning is pivotal in achieving this:
- Understanding User Behavior: AI algorithms analyze user data to discern patterns and preferences. This deep understanding aids in creating more empathetic and user-centric designs.
- Responsive Design: AI enables design elements to adapt to users' emotional states. For instance, a chatbot might alter its responses based on the user's mood, inferred from their input.
- Anticipatory Interfaces: Machine learning helps design interfaces that anticipate user needs. This proactivity results in smoother, more intuitive user experiences, where the system often addresses needs before the user explicitly expresses them.
Incorporating these elements of AI and machine learning in interaction design leads to more empathetic, responsive, and personalized user experiences. This fusion of technology and empathy significantly enhances the user's engagement with digital platforms.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Integrating empathy into technology brings significant benefits but presents unique challenges and ethical considerations.
1. Balancing Data Collection for Empathy with User Privacy Concerns
Empathetic technology requires extensive data to understand users. Yet, collecting this data raises privacy concerns. Users often worry about how a company uses and stores their data. A recent report by the Pew Research Center found that 73% of adults are concerned about how companies use their data. Companies must follow transparent data practices to address this and give users control over their data. Opt-in options and transparent privacy policies help companies win users' trust through full disclosure.
2. Addressing Biases in AI Algorithms for Fair and Unbiased Empathy
AI algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate biases that may lead to unfair user experiences. For instance, facial recognition technology has faced criticism for racial biases. To combat this, developers must use diverse data sets and regularly audit AI systems for biases. Implementing ethical guidelines in AI development is crucial to ensure fair and unbiased empathetic responses.
3. Ensuring Transparency and User Consent in Empathetic Technology
Transparency and user consent are paramount in empathetic technology. Users should be aware of how their data informs the technology's responses. For example, if an AI system uses emotional analysis, users must consent to this and understand its implications. Clear communication about the technology's capabilities and limitations is essential for building trust and ensuring ethical use.
Case Studies of Empathetic Design in Action
Empathetic design can transform user experiences. Let's explore some examples and learn from their outcomes.
1. Spotify's Personalized Playlists
Spotify employs algorithms to tailor playlists for individual users. This approach makes users feel understood, as the playlists often reflect their current mood or music preferences. This personal touch has led to higher engagement and user satisfaction.
2. Duolingo's Adaptive Learning
Duolingo adapts to each user's learning pace and style. The app identifies areas where a user struggles and adjusts the difficulty accordingly. This tailored learning experience supports users and motivates them to continue learning.
3. Zara's Augmented Reality Displays
Zara introduced augmented reality displays in its stores that allow customers to see how clothes look on models by scanning a barcode. This immersive experience makes shopping more interactive and engaging to increase customer interest and store visits.
4. Healthcare Chatbots
Some healthcare services use chatbots for initial patient interactions. These chatbots can assess symptoms and provide preliminary advice. However, if not carefully implemented, they can misinterpret patient emotions or needs, potentially causing frustration or misinformation.
From these cases, we see that empathetic design can significantly enhance user experience to increase adoption and satisfaction. However, unsuccessful implementations remind us that understanding and accurately responding to user needs is a delicate balance that requires careful consideration and ongoing refinement.
Empathy in Customer Support and Service Design
Empathy plays a crucial role in customer support and service design. Training customer support teams in empathetic interactions involves teaching active listening, understanding diverse customer perspectives, and responding sensitively. For instance, Ritz-Carlton empowers its employees to spend up to $2,000 per incident to resolve complaints or enhance their stay without manager interference. It shows deep understanding and responsiveness to customer needs.
Incorporating empathy into chatbots and automated customer service is another area of focus. Companies are programming chatbots to recognize and respond to emotional cues and make interactions more human-like. An example is KLM Royal Dutch Airlines' chatbot, which handles over 16,000 weekly customer interactions. It offers timely and personalized responses.
Empathetic service greatly influences customer loyalty and brand perception. According to a study by American Express, customers are willing to spend 17% more with companies that provide excellent service. This increased spending is often a result of feeling valued and understood through empathetic interactions. Such a service retains customers while transforming them into enthusiastic advocates for the brand. This shift in customer behavior underscores the importance of empathy in building solid and loyal customer relationships.
Measuring and Evaluating Empathy in Design
Measuring and evaluating empathy in design helps refine products and services to meet user needs better.
1. Develop Metrics for Assessing Empathetic Impact
Evaluating empathy in design involves creating specific metrics. These metrics help you understand how designs affect users emotionally.
- First, consider users' emotional reactions to a design. Are they positive, negative, or neutral? This reaction is crucial.
- Next, measure user engagement. How long do users interact with the design? More time often means higher empathy. Gather user feedback. Ask direct questions about their experience. Analyze this feedback for emotional content.
- Another critical metric is usability. User-friendly designs usually show higher empathy.
- Lastly, observe changes in user behavior. Does the design inspire action or change in attitude? This change indicates a practical, empathetic design.
These metrics offer a comprehensive view of empathetic impact in design.
2. User Testing Methodologies for Evaluating Emotional Responses
User testing helps you evaluate emotional responses to design. It helps understand how real users react emotionally to a product or design. Some methodologies for user testing include:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Simple tools to gauge users' feelings about the design. Questions should be straightforward and focus on emotional responses.
- Interviews: One-on-one discussions provide deeper insights into users' emotional reactions. They allow for detailed feedback and understanding of users' experiences.
- Observation: Watching how users interact with the design in a natural setting. This method offers unfiltered insights into their emotional responses.
- Usability Tests: These tests focus on how users perform tasks using the design. Observing frustrations or satisfaction can reveal emotional impacts.
- A/B Testing: Comparing two design versions to see which evokes a better emotional response. This method is data-driven and provides precise results.
You can combine different methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of users' emotional experiences.
3. Iterative Design Based on User Feedback and Emotional Analytics
Designers can use user feedback and emotional analytics for iterative improvements. This process involves making adjustments based on user input and then re-evaluating the design's emotional impact. For instance, a website might alter its layout based on user feedback about its emotional appeal and usability and then conduct further tests to assess the effectiveness of these changes.
Through these methods, designers can ensure that their products resonate with users emotionally. It may lead to more meaningful and satisfying user experiences.
Future Trends in Humanizing Technology
The future of humanizing technology is poised to bring remarkable changes, particularly in how technology understands and interacts with human emotions.
1. Emotional Intelligence in AI
AI is evolving to perform tasks and understand human emotions. Emotional intelligence in AI involves algorithms that can detect and respond to human feelings, leading to more intuitive and helpful interactions. For example, AI in customer service could evolve to detect customer frustration or satisfaction and adapt its responses accordingly.
2. Innovations in Wearables and Biometric Technology for Emotion Sensing
Wearables and biometric technologies are advancing to sense emotional states. Smartwatches could monitor physiological signals such as heart rate or skin temperature to infer emotional states like stress or relaxation. This technology can improve health monitoring, personalize user experiences, and even assist in mental health management.
3. Role of Empathy in the Future of Human-Computer Interaction
Empathy will play a crucial role in the evolution of human-computer interaction. Future interfaces may become more responsive to emotional cues, creating more natural and engaging user experiences. We might see interfaces that adjust content, tone, and interaction style based on the user's emotional state.
Conclusion
The significance of empathy in user experiences is undeniable. It transforms technology from a tool to a relatable companion that understands and responds to our emotional needs. This journey towards more humane and emotionally intelligent technology design is beneficial and essential. It fosters deeper connections between users and technology, enhancing satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
As we look forward, the encouragement is clear: to continue innovating and integrating empathy into every aspect of technology design. This shift promises a future where technology not only serves us functionally but also understands and resonates with us on an emotional level.
